认 证:工商信息已核实
访问量:206673
德国Attocube Systems AG公司成立于2002年,作为纳米科学领域年轻的仪器供应商,Attocube Systems AG以其掌握的纳米精度定位**成果和强大的技术实力,在短短的几年中研制开发了低震动无液氦磁体与恒温器、多种低温磁场下工作的扫描探针显微镜、极端环境应用纳米精度位移器、皮米精度位移激光干涉器等系列产品,深受用户赞誉。自成立以来,Attocube Systems AG已经获得了许多荣誉,包括Finalist for the 27th Innovation Award of the German Ecomomy 2007和 ****00 Innovation Award 2013 等。
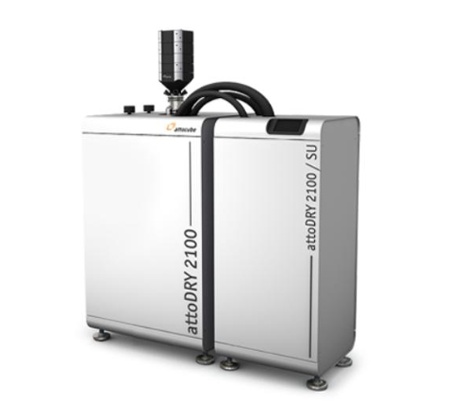
无液氦低温强磁场扫描探针显微镜
| 德国attocube公司推出的attoDRY Lab系列无液氦低温强磁场扫描探针显微镜系统基于attoDRY系列无液氦强磁场超低震动恒温器和多种扫描探针显微镜插件,特别适应于低温光学实验、扫描探针显微镜等应用,产品优异的稳定性为超高分辨率的表面表征研究奠定了坚实的基础。不止于此,产品还*早集成了简单易用的触摸屏控制系统以方便自由控制温度大小与磁场强度的商业化恒温器。扫描探针显微镜插件包括:attoAFM/MFM/cAFM/PRFM原子力、磁力、导电力、压电力显微镜;attoCFM共聚焦显微镜;Raman与光致发光谱;atto3DR双轴旋转平台等。 |
参数与技术特点:
+ 无液氦,闭路可循环系统
+ 独特设计,超低震动(0.12 nm RMS)
+ 温度范围:1.5 K...300 K 或 4 K...300 K
+ 磁场强度:**可达15T
+ 多功能测量平台:AFM/MFM/ct-AFM/PRFM/CFM/RAMAN
+ 超高温度稳定性
+ 全自动控制,触摸屏控制
+ 快速冷却:1-2小时样品冷却
相关阅读:
2、低温强磁场原子力/磁力/扫描霍尔显微镜 - attoAFM/attoMFM/attoSHPM
3、磁共振显微镜/低温强磁场磁共振显微镜 - attoCSFM
部分发表文献:
2. Chaoyang Lu et.al, Towards optimal single-photon sources from polarized microcavities. Nature Photonics, 13, 770–775 (2019)
3. Yuanbo Zhang et. Al, “Signatures of tunable superconductivity in a trilayer graphene moiré superlattice”Nature, 572, 215-219 (2019)
4. P. Maletinsky et. Al, Probing magnetism in 2D materials at the nanoscale with single-spin microscopy, Science, 364, 973 (2019)
5. Haomin WANG et al, “Isolating hydrogen in hexagonal boron nitride bubbles by a plasma treatment”.Nature communications, 10, 2815 (2019)
6. Mingyuan Huang et.al, Magnetic Order-Induced Polarization Anomaly of Raman Scattering in 2D Magnet CrI3, Nano Letters, 2020,20,1, 729-734
7. Alexander H?gele et. al, Cavity-control of interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures, Nature communications, 2019,10:3697.
8. Hanxuan Lin, et al. Unexpected Intermediate State Photoinduced in the Metal-Insulator Transition of Submicrometer Phase-Separated Manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 267202(2018)
9. Chaoyang Lu et.al, High-efficiency multiphoton boson sampling. Nature Photonics, 11, 361-365, (2017)
10. K. Yasuda, et al. Quantized chiral edge conduction on domain walls of a magnetic topological insulator. Science 2017, 358, 1311-1314
11. Zhu, Y. et al. Chemical ordering suppresses large-scale electronic phase separation in doped manganites. Nature communications, 2016,7:11260.
12. Yang, W.;et al. Electrically Tunable Valley-Light Emitting Diode (vLED) Based on CVD-Grown Monolayer WS2. Nano Letters 2016, 16, 1560-1567.
13. Surajit Saha; et al. Long-range magnetic coupling across a polar insulating layer, Nature communications, 2016,7:11015.
14. He, Y. M.; et al. Single quantum emitters in monolayer semiconductors.Nature Nanotechnology 2015, 10, 497-502.
16. Proton magnetic resonance imaging using a nitrogen–vacancy spin sensor. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015,10,120-124.
17. Nanoscale nuclear magnetic imaging with chemical contrast. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10, 125-128.
18. Observation of biexcitons in monolayer WSe2. Nature Physics, 2015, 11, 477-481.
19. Visualization of a ferromagnetic metallic edge state in manganite strips. Nature Communications, 2015, 6:6179.
20. Observation of Excitonic Fine Structure in a 2D Transition-Metal Dichalcogenide Semiconductor. ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 647-655.
21. Energy losses of nanomechanical resonators induced by atomic force microscopy-controlled mechanical impedance mismatching. Nature Communications, 2014, 5:3345.
22. Deterministic and electrically tunable bright single-photon source. Nature Communications, 2014, 5:3240.
23. Dynamic Visualization of Nanoscale Vortex Orbits. ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 2782-2787.
24. Transition from slow Abrikosov to fast moving Josephson vortices in iron pnictide superconductors. Nature Materials, 2013, 12, 134-138.
25. Stray-field imaging of magnetic vortices with a single diamond spin. Nature Communications, 2013, 4:2279.
26. Realization of pristine and locally tunable one-dimensional electron systems in carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8, 569-574.
27. Strong magnetophonon resonance induced triple G-mode splitting in graphene on graphite probed by micromagneto Raman spectroscopy. Physical Review B, 2013, 88, 165407.
28. Origin of negative magnetoresistance of GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As core-shell nanowires. Physical Review B, 2013, 87, 245303.
29. Magnetic Imaging on the Nanometer Scale Using Low-Temperature Scanning Probe Techniques. Microscopy Today, 2011, 19, 34-38.
30. Visualization of charge transport through Landau levels in graphene. Nature Physics, 2010, 6, 870-874.
部分用户列表
attocube公司产品以其稳定的性能、极高的精度和良好的用户体验得到了国内外众多科学家的认可和肯定。attocube公司的产品在国内也得到了低温、超导、真空等研究领域**科学家和研究组的欢迎......
北京大学 | 清华大学 |
中国科技大学 | 南京大学 |
中科院物理所 | 中科院半导体所 |
中科院武汉数学物理所 | 上海同步辐射中心 |
中科院上海应用技术物理研究所 | 北京理工大学 |
复旦大学 | 哈尔滨工业大学 |
中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所…… | |
- 推荐产品
- 供应产品
- 产品分类